Artificial Intelligence streamlining stroke diagnosis for Latvian medical professionals
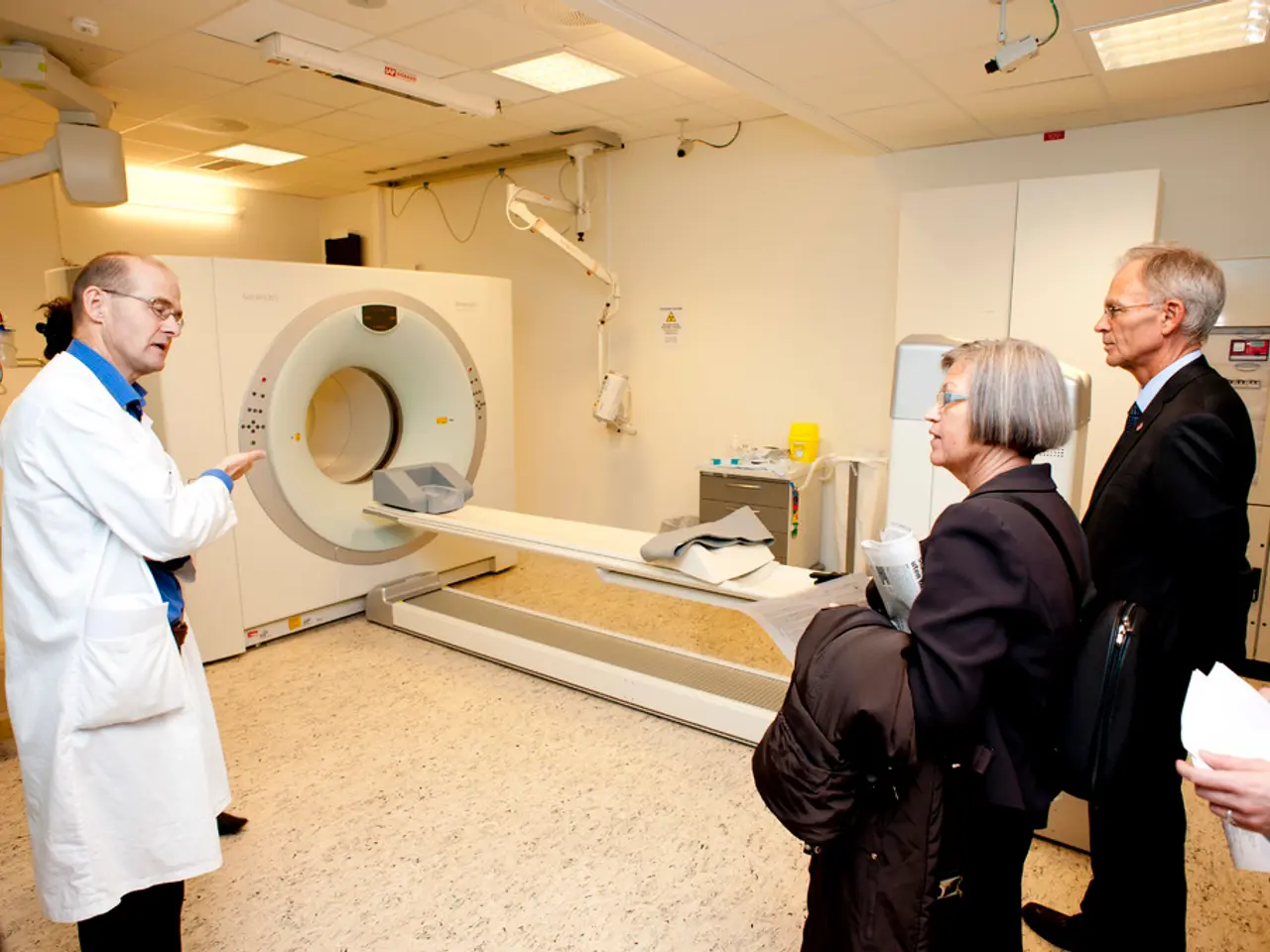
In the bustling Emergency Medicine Center of Pauls Stradins Clinical University Hospital, the workload is heavy, with over 200 patients admitted daily. Among these patients, approximately 1,000 are diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke each year. To help alleviate the pressure and ensure timely and accurate diagnoses, a groundbreaking AI solution called "Sinapse" has been integrated into the hospital's daily work.
Developed by Kārlis Kupčs, the head of the Institute of Diagnostic Radiology at the hospital, along with Andris Veis and the creator of the prototype artificial intelligence solution "Apply", "Sinapse" has been reviewing over 1,000 patients' radiology examinations. The AI solution is designed to assist radiologists in evaluating acute ischemic stroke examinations, which can have significant impacts on patient outcomes.
"Sinapse" is capable of recognizing abnormalities such as bruises, hematomas, or hemorrhages, drawing doctors' attention to cases where signs of stroke are visible. The AI solution is fully integrated into doctors' work, requiring no additional time from specialists.
In less than a year, the accuracy of "Sinapse" has increased by 13%, reaching 93% accuracy. Kupčs is confident that "Sinapse" will become a regular part of the daily work rhythm and continue to develop. However, implementing "Sinapse" in other institutions requires both financial and human resources for training.
Discussions are underway to introduce "Sinapse" into other medical institutions. The developers of "Sinapse" are currently working on training the tool to accurately identify and name these abnormalities. They estimate that it could soon recognize other diseases and aid hospital doctors in regions.
AI technologies are increasingly used to analyze complex imaging data and clinical records to improve diagnostic accuracy. Major medical technology companies like Abbott are integrating AI to enhance cardiovascular imaging to guide interventions and personalized risk scoring. Despite advances, challenges remain in making AI models fully reliable and ethically safe in critical medical decisions, including those involving brain and neurological conditions.
For accurate, up-to-date information on "Sinapse," it may be necessary to consult recent scientific publications, company announcements, or clinical trial databases directly associated with that technology. The search results provide relevant context on AI applications in medical diagnostics and imaging but do not mention "Sinapse" specifically or its deployment in stroke recognition.
- Kārlis Kupčs, alongside Andris Veis and the inventor of "Apply", created "Sinapse", an AI solution designed to aid radiologists in evaluating acute ischemic stroke examinations.
- "Sinapse" is integrated into the daily work of doctors at Pauls Stradins Clinical University Hospital, assisting in the recognition of abnormalities such as bruises, hematomas, or hemorrhages associated with stroke.
- In just under a year, the accuracy of "Sinapse" has improved by 13%, reaching 93% accuracy, making it a promising addition to the diagnostic tools used in chronic diseases and health-and-wellness practices.
- The team behind "Sinapse" is working to expand its capabilities, training the AI to identify and name various abnormalities beyond stroke, potentially aiding in the diagnosis of medical-conditions across a wide range of disciplines.
- The integration of AI technologies, like "Sinapse", in medical institutions could revolutionize the field, particularly in the analysis of complex imaging data and clinical records related to chronic diseases, cancer, heart diseases, or even mental health issues, all encompassing the broader spectrum of health-and-wellness and medical-conditions.