Benefits, Nutritional Information, Dietary Usage, and Potential Hazards of Carrots
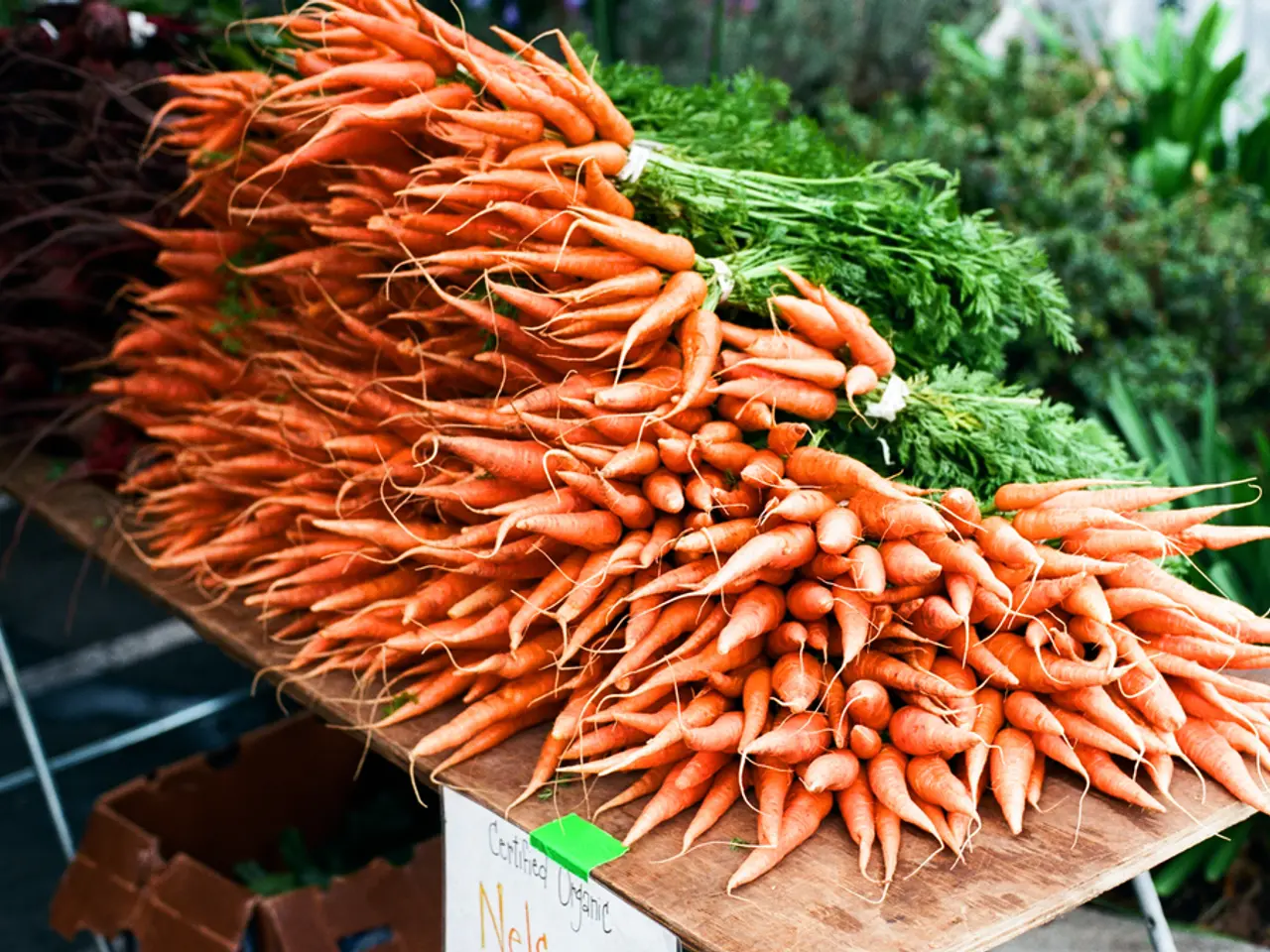
Carrots, known for their vibrant orange hue, are not just a delicious vegetable, but a nutritional powerhouse that offers a variety of health benefits.
Rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, carrots play a significant role in maintaining overall health. One medium-sized, raw carrot contains approximately 251 calories, 5.8 grams of carbohydrates, 1.7 grams of fiber, and is a good source of essential minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, and potassium.
The American Heart Association recommends eating more foods that contain potassium, such as carrots, to help reduce the risk of high blood pressure and other cardiovascular issues. Eating vegetables high in fiber, such as carrots, may also help reduce a person's risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Carrots are particularly renowned for their contribution to eye health. They contain the antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin, which protect the eyes from oxidative stress and potentially support the prevention of age-related macular degeneration. Additionally, consuming carrots may lower levels of low-density lipoprotein, or "bad" cholesterol, which can contribute to heart health.
However, carrots offer more than just eye and heart benefits. The vitamin C in carrots contributes to collagen production, essential for wound healing and maintaining the body's health. A balanced diet that provides adequate vitamin C can help fight disease and infection.
It's important to note that while carrots are beneficial, they are not a cure-all. A lack of vitamin A can lead to xerophthalmia, a progressive eye disease, and some people may be allergic to compounds in carrots, causing symptoms such as hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing.
Moreover, eating large amounts of fiber or rapidly increasing fiber intake may cause gastrointestinal issues like bloating and constipation. Therefore, it's always advisable to introduce new foods into your diet gradually.
Organic carrots have been found to have higher levels of vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, phosphorus, and calcium compared to non-organic carrots. This suggests that opting for organic carrots may provide even more health benefits.
Furthermore, a diet rich in carotenoids, the pigments that give carrots their colour, may lower the risk of prostate cancer. Carrots also contain vitamin K, calcium, and phosphorus, which are beneficial for bone health and may help prevent osteoporosis.
Lastly, the antioxidant effects of dietary carotenoids may reduce the risk of certain cancers. Consuming a high fiber diet may lower the risk of colorectal cancer, further emphasising the importance of incorporating carrots and other fiber-rich foods into your diet.
In conclusion, carrots offer a myriad of health benefits beyond their well-known role in maintaining eye health. From supporting heart health to boosting the immune system and aiding in bone health, carrots are a versatile and nutritious addition to any diet.
- The rich nutritional content of carrots, including vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, predictively aids in maintaining digestive health, skin care, health-and-wellness, fitness-and-exercise, and nutrition.
- A diet that includes carrots, particularly because of their high fiber content, may reduce the risk of obesity and rheumatoid arthritis, promoting overall fitness and exercise.
- Carrots are known to contain essential minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, and potassium, benefiting bone health and potentially preventing osteoporosis.
- The antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin found in carrots contribute to the prevention of age-related macular degeneration and support eye health.
- Consuming carrots may lower levels of low-density lipoprotein, or "bad" cholesterol, which can contribute to heart health.
- The vitamin C in carrots is essential for wound healing, collagen production, and fighting diseases and infections.
- A balanced diet that provides adequate vitamin C, as found in carrots, can help prevent depression and potentially support the prevention of Alzheimers.
- The antioxidant effects of dietary carotenoids found in carrots may reduce the risk of certain cancers, such as prostate cancer, and lower the risk of colorectal cancer.