Canned vs. Dried Beans: Which Is the Healthier, More Convenient Choice?
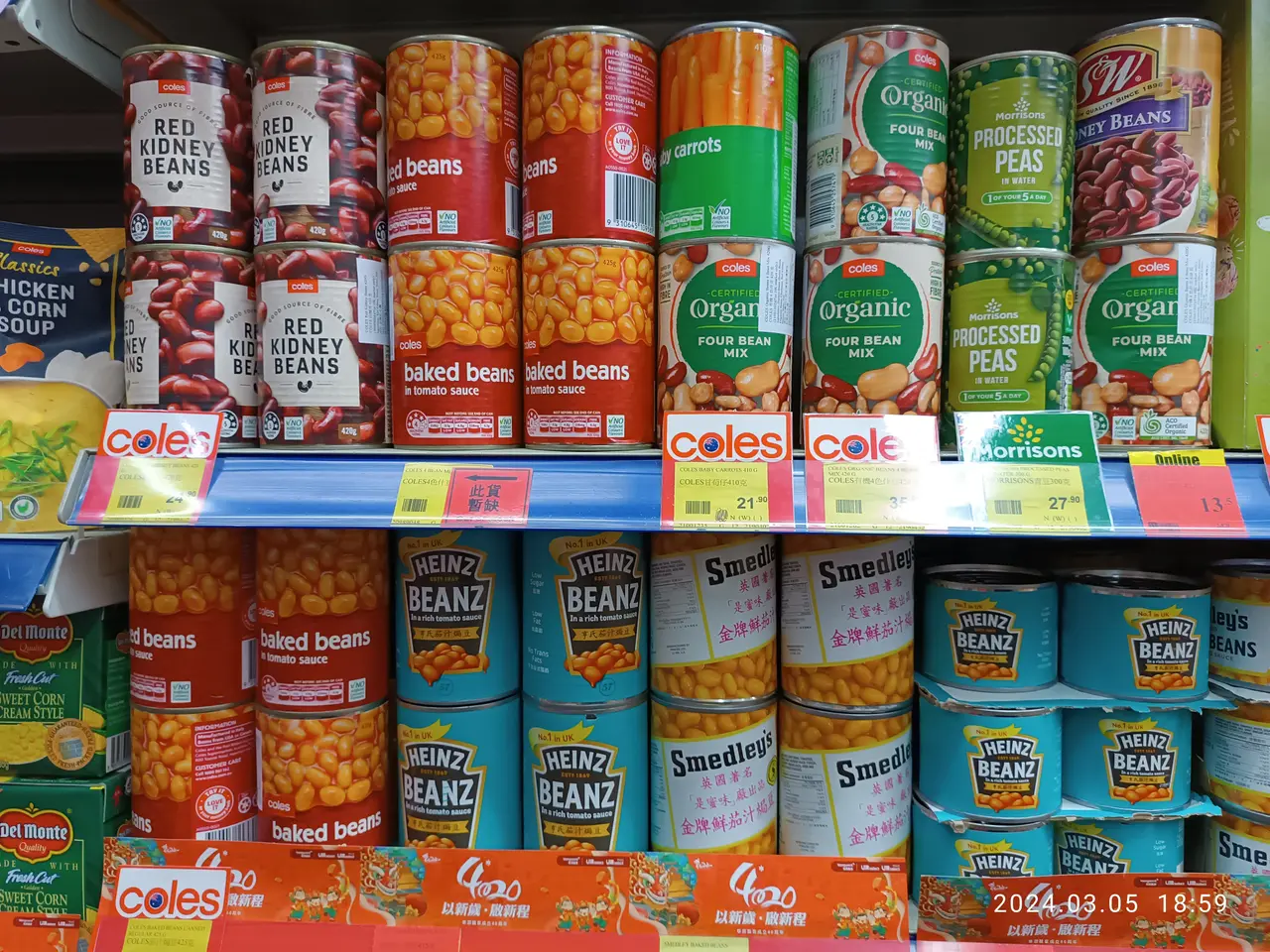
Beans are a nutritious and budget-friendly food, available in two main forms: dried and canned. Both offer health benefits, but each has distinct advantages depending on how they’re prepared and used. Understanding the differences can help people choose the best option for their diet.
Canned beans provide convenience, with a long shelf life and no need for soaking or extended cooking. They are ready to use straight from the tin, making them ideal for quick meals. However, they often contain higher sodium levels, though rinsing and draining can cut sodium by up to 40 percent. This process also helps remove some oligosaccharides, which can ease digestion.
Dried beans, on the other hand, give cooks more control over flavour, texture, and preparation. Soaking and slow cooking them breaks down oligosaccharides further, improving digestibility. While both canned and dried beans offer similar nutrients, dried beans retain slightly more water-soluble vitamins, like B vitamins, as canned varieties lose some during high-heat processing. Neither form is universally better, but canned beans may encourage more regular consumption due to their ease of use. Both types are rich in fibre, which supports gut health and helps stabilise blood sugar levels.
Beans remain a versatile and affordable staple, whether chosen fresh or canned. Those watching their sodium intake can opt for no-salt-added or reduced-sodium canned varieties. For maximum nutrient retention and customisation, dried beans offer flexibility, while canned beans deliver speed and convenience.