Covid-19 and Tongue Discomfort: Potential Connections Explored
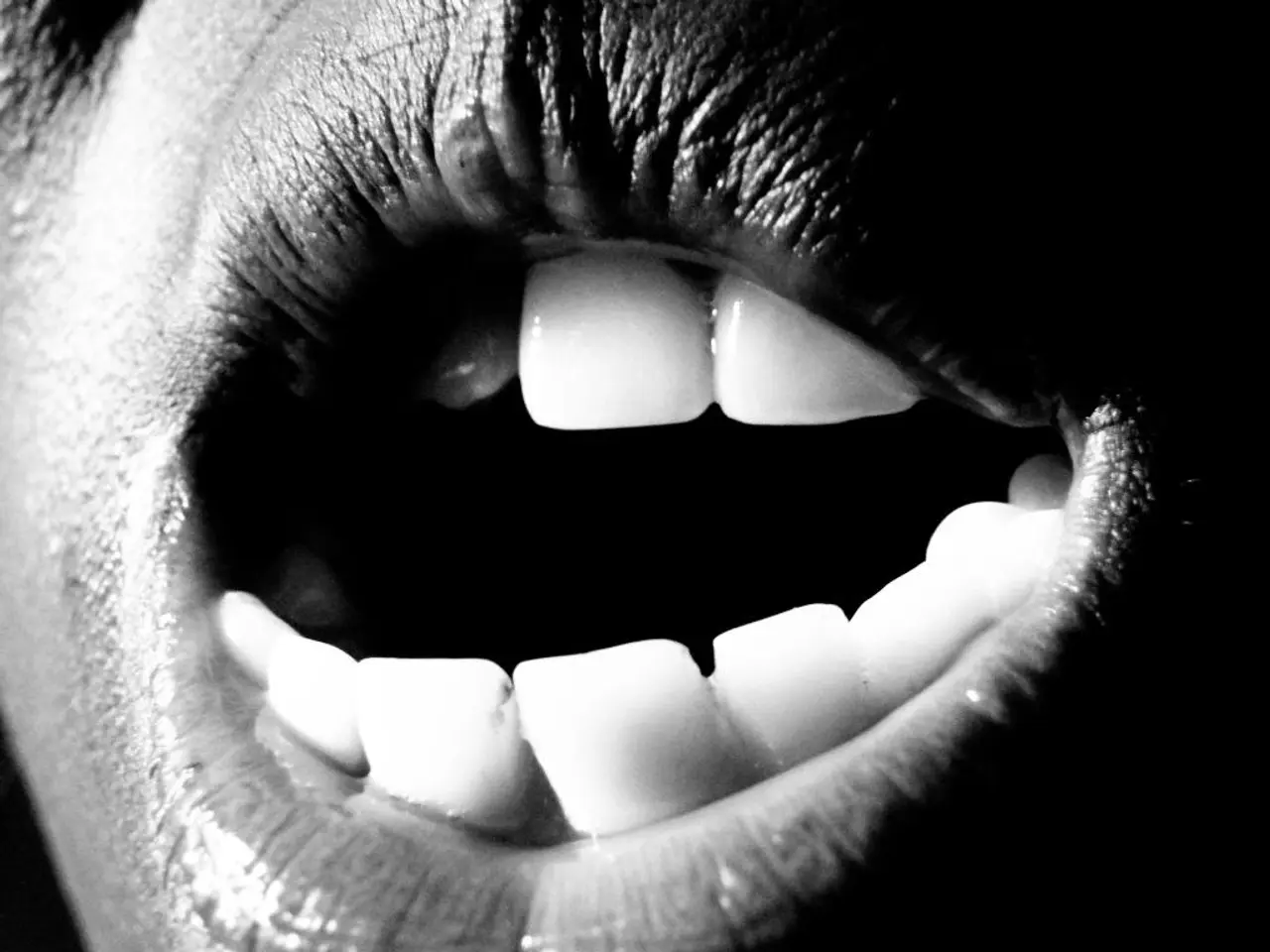
COVID Tongue, a less common but notable symptom of COVID-19, is characterised by swelling, a burning sensation, and a rough or bumpy surface on the tongue. This condition may also present as geographic tongue or tongue mucosal changes, ulcers, pain, and white patches on the tongue surface.
Causes of COVID Tongue
The causes of COVID Tongue are multifaceted. Direct viral infection and inflammation of the oral mucosa by SARS-CoV-2 are primary causes. Secondary infections such as herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) or candidiasis (oral thrush) can co-occur or exacerbate symptoms.
In some cases, the post-COVID condition (Long COVID) can feature persistent tongue changes related to immune dysregulation or nerve involvement, such as trigeminal nerve sensitivity. Additionally, medications used to treat COVID-19 may contribute to oral symptoms, for example, causing burning mouth or taste changes.
Treatments for COVID Tongue
Treatment for COVID Tongue focuses on symptom control, addressing secondary infections, and occasionally novel therapies like photobiomodulation (light therapy). Antiviral treatment such as acyclovir may be prescribed if HSV-1 coinfection is confirmed, although some cases show resistance to antiviral therapy.
Over-the-counter remedies such as antifungal, antiviral, and antibacterial mouthwashes, saliva substitutes, lozenges, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help with specific symptoms. Good oral hydration and hygiene, as well as management of secondary infections like candidiasis, are also important for symptom relief.
Monitoring and Care
For persistent or severe symptoms, ongoing monitoring and care by dental or oral medicine specialists are advised. A 2022 study investigated oral adverse events following COVID-19 and seasonal influenza vaccinations.
It's important to note that COVID Tongue may not be a specific symptom of COVID-19, but rather a manifestation of disease progression. Other common symptoms of COVID-19 include coughing, shortness of breath, fatigue, and nausea. Oral thrush, oral herpes, allergies, bacterial, fungal, or viral infections can cause symptoms similar to COVID Tongue.
If COVID Tongue symptoms persist after two weeks, it is best to consult a doctor. Treating COVID-19 can alleviate symptoms, but there is currently no specific treatment for COVID Tongue.
In conclusion, COVID Tongue arises from a combination of viral infection effects directly on the tongue, secondary infections, immune responses, and treatment side effects. Management focuses on symptom control, addressing secondary infections, and occasionally novel therapies like photobiomodulation.
Science has revealed that COVID Tongue, a symptom of COVID-19, can be linked to medical-conditions such as ulcers, secondary infections, or health-and-wellness issues related to nerve involvement or medication side effects. Furthermore, in circumstances where COVID Tongue persists for an extended period, it may necessitate monitoring and care from medical professionals, and prompt medical advice is advisable to address this health-and-wellness challenge.