Essential Facts About Hepatitis A and B
Traveling to various destinations can be an exciting experience, but it's essential to take precautions to protect your health. Two vaccinations that are often advisable for travelers are those for Hepatitis A and B.
Hepatitis A Vaccination
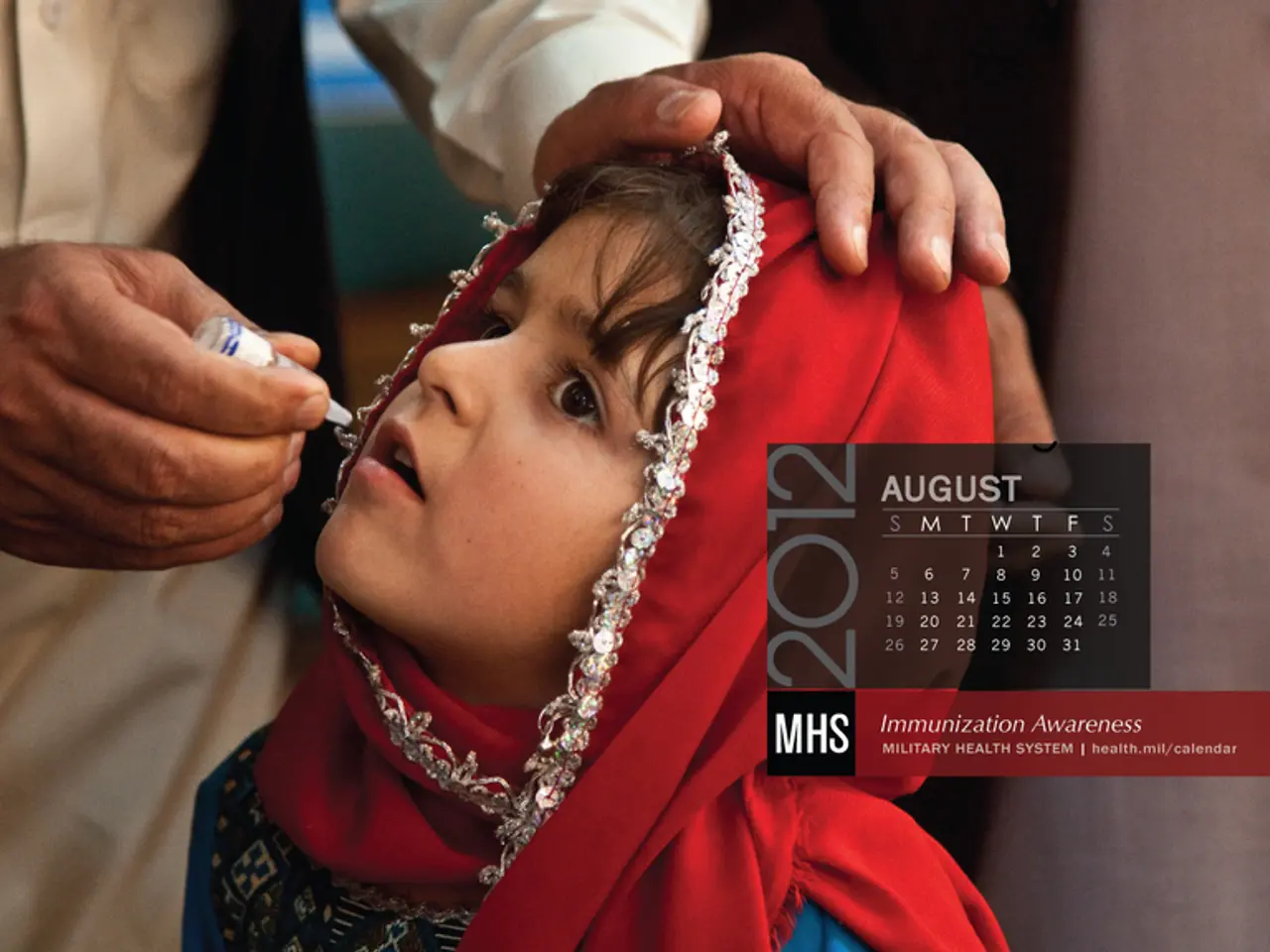
Hepatitis A is primarily spread through contaminated food and water, making it common in many developing regions, including parts of South America and Southeast Asia. To ensure protection, the German Liver Foundation recommends vaccination for all travelers aged 1 year and older going to countries with a risk of Hepatitis A.
Typically, the vaccination involves two doses spaced at least six months apart for long-term protection. One dose offers short-term protection useful for imminent travel. For infants aged 6–11 months, one dose before departure is recommended, followed by the routine two-dose series between 12 and 23 months for long-term immunity. Unvaccinated travelers 12 months or older should get the first dose as soon as travel is considered.
Hepatitis B Vaccination
Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood and bodily fluids, with the risk increased by activities such as emergency medical treatment, dental work, or sexual contact abroad. Many older adults (born before universal vaccination programs) may lack immunity and should consider vaccination before travel.
Vaccination schedules vary depending on age and prior doses. For children and adolescents, a two-dose series (six months apart) or a three-dose series at 0, 1–2, and 6–18 months is usually recommended. Adults can receive a combined Hepatitis A and B vaccine as a three-dose series (0, 1, and 6 months) or an accelerated four-dose series for faster protection.
Additional Considerations and Risk Factors
Destinations with high or intermediate endemicity for Hepatitis A or B, such as much of South America, Cambodia, and other developing countries, warrant vaccination. For older travelers or those with immunosuppression, consultation with healthcare providers is recommended to assess vaccine risks and benefits.
Other routine vaccinations (MMR, DTP, polio, etc.) are also important to ensure before travel, as well as weighing the risks and benefits of yellow fever vaccination in certain destinations, especially for older adults due to the risk of adverse events.
Summary Table of Vaccination Schedules for Travelers
| Vaccine | Typical Schedule | Notes | |--------------------|-----------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------| | Hepatitis A | 2 doses, ≥6 months apart | 1 dose may be given for short-term travel; infants 6–11 months get 1 dose pre-travel | | Hepatitis B | 3 doses at 0, 1–2, 6–18 months or 2-dose (6-month interval) for adolescents | Adults may use combined Hep A/B vaccine (3 or 4-dose schedules) | | Hepatitis A & B (Combined - Twinrix) | 3-dose: 0, 1, 6 months; or accelerated 4-dose: 0, 7, 21–30 days plus booster at 12 months | Useful for travelers needing both vaccines |
In conclusion, Hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all travelers over 1 year old to many at-risk destinations, with an accelerated schedule for infants and last-minute travelers. Hepatitis B vaccination is advised especially for those with increased exposure risk or lack of prior immunization. Travelers should consult healthcare providers or travel clinics for individualized advice based on destination, vaccination history, and personal risk factors.
- Science plays a crucial role in protecting travelers' health and wellness, as demonstrated by the Hepatitis A and B vaccinations that are often advised for those venturing to countries with a risk of Hepatitis transmission.
- For individuals who may lack immunity to Hepatitis B and are planning to travel, receiving the medical-conditions-related vaccination is essential to prevent Hepatitis B transmission through blood and bodily fluids, especially in destinations where the disease is prevalent.