Frequent Consumption of This Specific Morning Meal, Recommended by Sleep Specialists
Improving Sleep Quality: Foods to Incorporate for Better Rest
A growing body of research suggests that certain foods and nutrients can significantly improve sleep quality and patterns. Here's a guide to the key players:
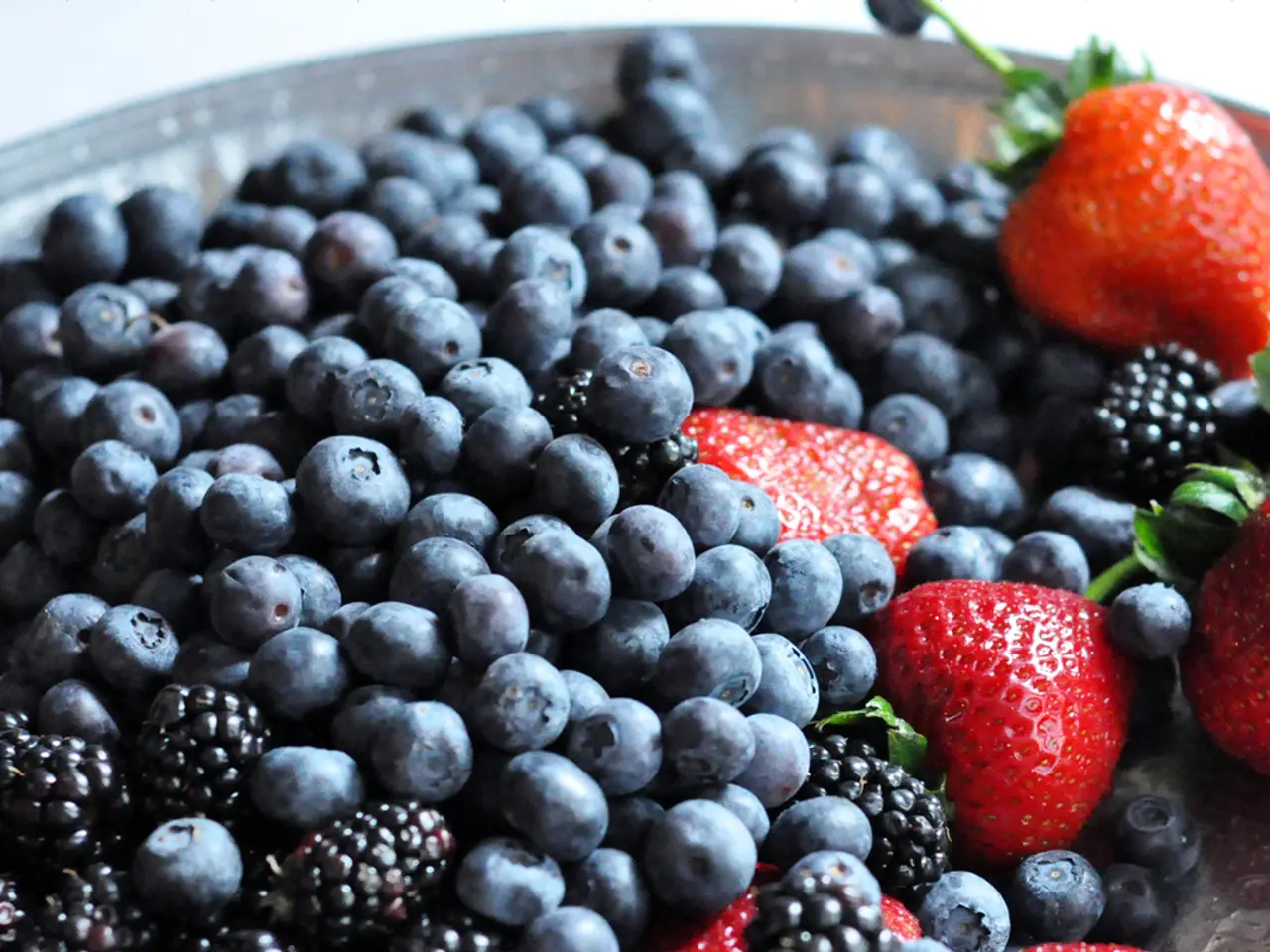
Fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel, sardines), high in omega-3 fats and vitamin D, can boost serotonin levels, supporting better sleep and daytime functioning [1][2].
Kiwi is another sleep-friendly food, containing serotonin and antioxidants like vitamin C, which help people fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer [1][2].
Almonds are a rich source of magnesium and melatonin, which help muscles relax and may reduce stress hormone cortisol, improving sleep [1][3][4].
Oats provide natural melatonin, magnesium, and tryptophan, and their complex carbs stabilize blood sugar and increase serotonin, promoting better sleep quality [1][3].
Chamomile tea contains apigenin, a relaxing antioxidant that may reduce nighttime awakenings and promote sleepiness [1][2].
Pumpkin seeds are rich in magnesium, tryptophan, zinc, and antioxidants, supporting serotonin and melatonin production crucial for sleep regulation [3][5].
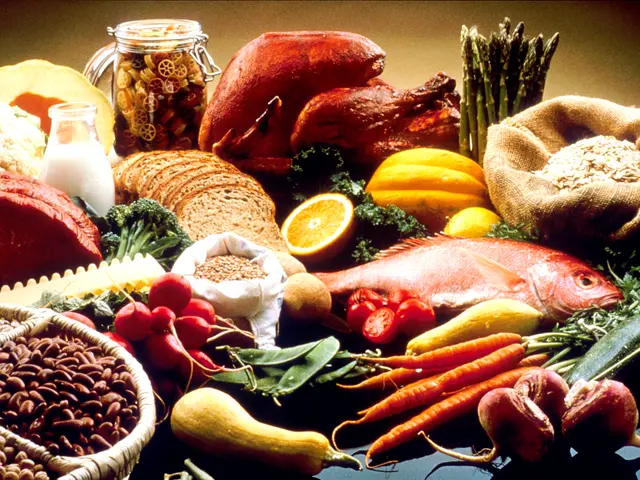
Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, supply magnesium, tryptophan, calcium, potassium, vitamin B6, and other antioxidants that support sleep and overall health [3][5].
Tart cherry juice contains melatonin and compounds that regulate sleep cycles, enhancing sleep quality [2][3].
Other noted sleep-friendly foods include pistachios, walnuts, turkey, chicken, eggs, Greek yogurt, tomatoes, mushrooms, and various nuts, due to their content of tryptophan, melatonin, or supportive minerals [3][4][5].
However, it's also important to avoid spicy, acidic, caffeinated, and high-fat foods near bedtime, as these can disrupt sleep by causing indigestion or overstimulation [2].
This information is based on various studies published in reputable journals such as the Nutrients, Western Journal of Nursing Research, Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, and The National Library of Medicine. For a comprehensive list of signs for emergency medical attention, please refer to the National Library of Medicine's website. Always remember that this information should be used in conjunction with professional medical advice.
For more insights on sleep-friendly foods and snacks, check out articles from Northwestern Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, and the National Sleep Foundation.
[1] The Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, "Fiber and Saturated Fat Are Associated with Sleep Arousals and Slow Wave Sleep." [2] Harvard Health Publishing, "Eating junk food may affect deep sleep." [3] The Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, "The Effects of Magnesium - Melatonin - Vit B Complex Supplementation in Treatment of Insomnia." [4] The Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition, "The association between cholesterol/saturated fat index (CSI) and quality of sleep, and circadian rhythm among overweight and obese women: a cross-sectional study." [5] The National Library of Medicine's list of signs for emergency medical attention.
- Incorporating science-backed foods like fatty fish, kiwi, almonds, oats, chamomile tea, pumpkin seeds, leafy greens, and tart cherry juice into one's diet can support better health-and-wellness and fitness-and-exercise, as these foods have been found to improve sleep quality and patterns.
- Sleep quality can be positively impacted by consuming nutrient-dense foods such as those rich in tryptophan, melatonin, magnesium, vitamin D, and various antioxidants, including fatty fish, kiwi, almonds, oats, chamomile tea, pumpkin seeds, and leafy greens, while avoiding spicy, acidic, caffeinated, and high-fat foods near bedtime to reduce the risk of indigestion and overnight stimulation.