How Your Gut Shapes Your Mind: The Science of the Brain-Gut Connection
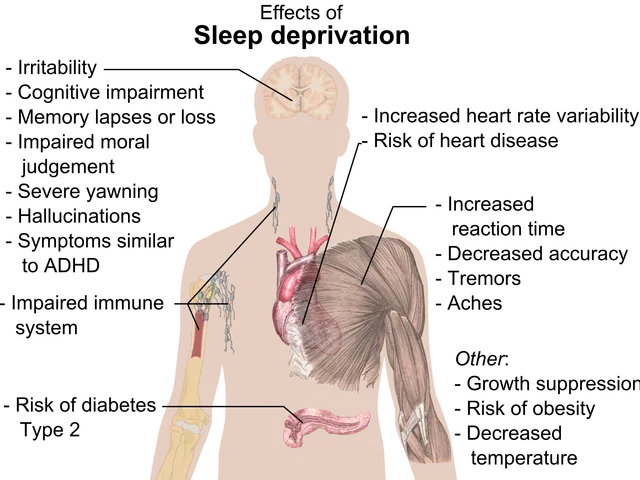
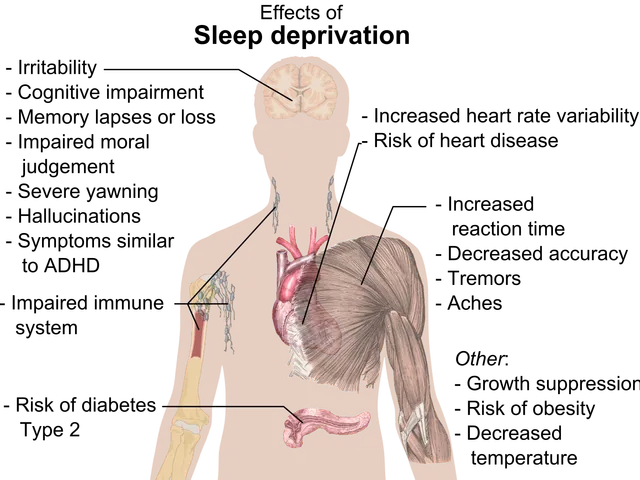
Scientists are unravelling the complex connection between gut health and mental well-being, with the gut-brain axis emerging as a key player. Imbalances in gut microbiota and disrupted communication pathways can contribute to mental health disorders like anxiety and depression, as well as physical conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease.
Researchers like Bradley Barth and Warren Grill are exploring electrostimulation therapies to restore disrupted gut-brain interactions, targeting conditions like depression and stress. Meanwhile, Dr. Kami Alexander Pekayvaz investigates the link between stress, the immune system, and cardiovascular diseases, which ties into gut-brain interactions. Other studies, like those at the University of Greifswald, delve into genetic and microbiome influences on depression via the gut-brain axis.
The gut's microbiota plays a crucial role in shaping overall health, including mental well-being. It produces neurotransmitters and regulates inflammation and immune responses. Chronic stress, however, can disrupt this balance, leading to inflammation and changes in gut permeability. To counter this, probiotics and dietary modifications can restore a healthy gut ecosystem, potentially improving brain function and mental health.
Understanding the gut-brain axis and its influence on mental well-being is vital for promoting overall wellness. By addressing gut health through probiotics and dietary modifications, we can potentially alleviate mental health disorders like anxiety and depression, and improve physical health conditions linked to gut-brain interactions.