Mexico’s organic farming triumphs while U.S. reapproves toxic paraquat
Mexico, a global leader in organic food production, maintains robust standards and a commitment to sustainable farming. Meanwhile, the U.S. has recently reapproved the toxic pesticide paraquat, raising concerns about health and food safety disparities between the two countries.
Mexico's dedication to organic farming has positioned it as one of the world's largest producers of organic food. It upholds stringent standards and promotes sustainable practices. In contrast, the U.S. has recently ruled paraquat permissible for agricultural use, despite its links to Parkinson's disease and other severe health issues. This decision has sparked criticism, as paraquat's toxicity is well-documented.
Regulatory differences between countries also impact food safety. In the EU and Australia, most food enzymes are regulated as processing aids, not additives. However, in the U.S., Canada, and Japan, all food enzymes are considered additives. This disparity leads to regulatory uncertainties and influences safety assessments and market approvals of foods.
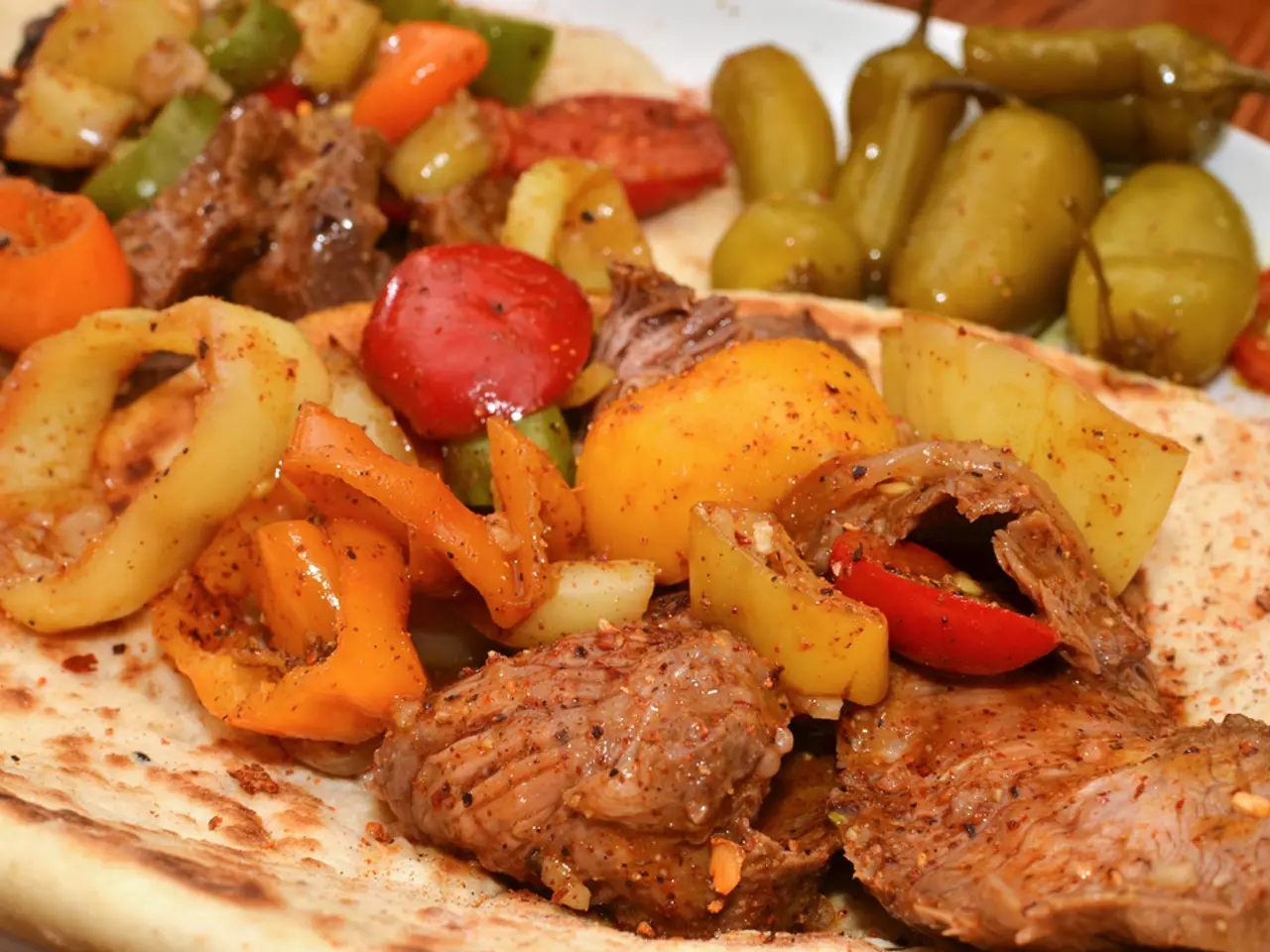
Industrial farming practices in the U.S. have led to a decline in the nutritional value of produce compared to decades ago. Meanwhile, Mexico's commitment to organic farming has resulted in produce that often tastes better and is more nutritious. For instance, U.S. tomatoes may look perfect but lack the flavor found in Mexican varieties.
Mexico is phasing out glyphosate, a controversial herbicide, under U.S. trade pressure. However, the process is slow. The European Union's regulatory body, the EFSA, takes a precautionary approach to food safety. In contrast, the U.S. allows products until harm is proven, leading to a higher prevalence of obesity, chronic illness, and cancers among younger adults.
Mexico has banned 183 highly hazardous pesticides and plans to prohibit an additional 35 toxic pesticides by 2025. It also bans several synthetic food dyes, preservatives, and practices like chlorine-washing of chicken that are common in the U.S. The EFSA has banned or refused approval for hundreds of agricultural products and chemical food additives that are legal in the U.S.
Mexico's commitment to organic food and stringent food safety standards stands in contrast to the U.S.'s recent decisions on paraquat and its more lenient regulatory approach. These differences highlight the importance of international cooperation in ensuring global food safety and sustainability.