Neuroscience Breakthrough: Sex-Specific Role of MMP-9 in Anxiety and Depression
Recent neuroscience breakthroughs have shed light on the complex interplay between genetics, behaviour, and emotional well-being. A study led by Senserrich and colleagues has delved into the role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in anxiety and depression, revealing significant sex differences that could pave the way for more personalised treatments.
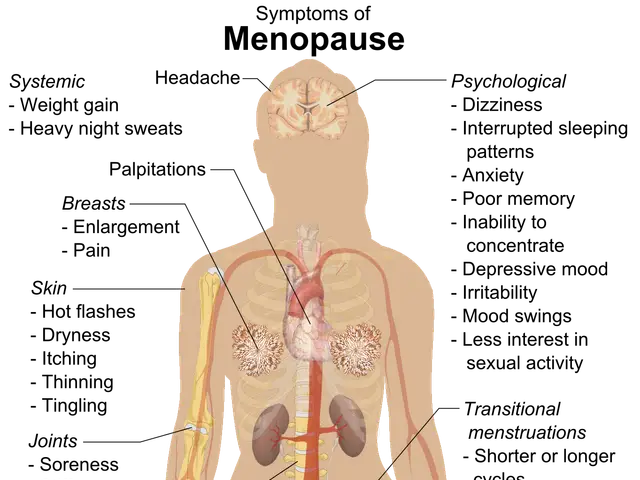
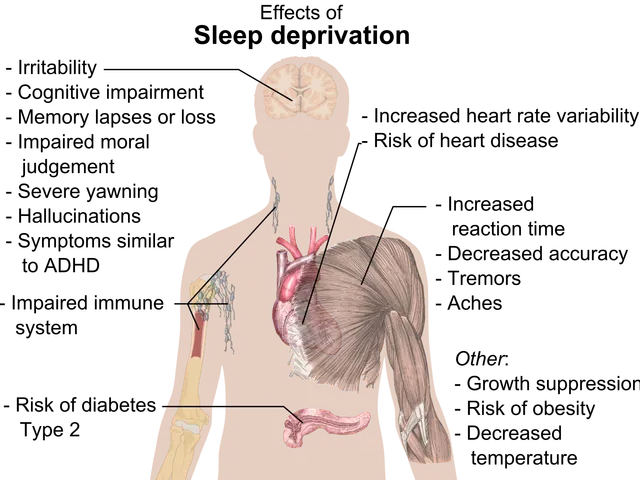
The study found that elevated MMP-9 levels in male mice exacerbated anxiety-like symptoms. Conversely, female mice displayed a different response, suggesting a protective factor meals. This sex-specific reaction is thought to be influenced by sex hormones, which may modulate brain plasticity and stress resilience. The research underscores the need for further investigation into sex differences in neurobiological frameworks to enhance understanding and treatment of mental health disorders. By exploring the interactions between MMP-9 and various genetic and epigenetic factors across sexes, new intervention pathways may be illuminated. The study proposes an integrated model where both biological and environmental factors shape mental health outcomes, emphasising the importance of a holistic approach to treatment.
The findings highlight the necessity for a sex-specific approach in psychological and pharmacological interventions for mood disorders. Future research should continue to investigate the role of MMP-9 and other biological factors in mental health, considering the influence of sex hormones and environmental factors to develop more effective, personalised treatments.
Read also:
- Actively Black's Lanny Smith Declares NYFW Show 'Not a Fashion Show', but a Civil Rights Tribute
- Upper Dublin Launches Tech Trek: A Digital Well-being Resource for Families
- Tom Holland: Christianity's Role in Shaping Western Thought
- Historian Ute Frevert Explores 'Constitutional Feelings' Among Far-Right AfD Voters