Potential Simplified Approach for Accurate Celiac Disease Diagnosis in Sight?
Celiac Disease Diagnosis: A Fresh Look with the WBAIL-2 Test
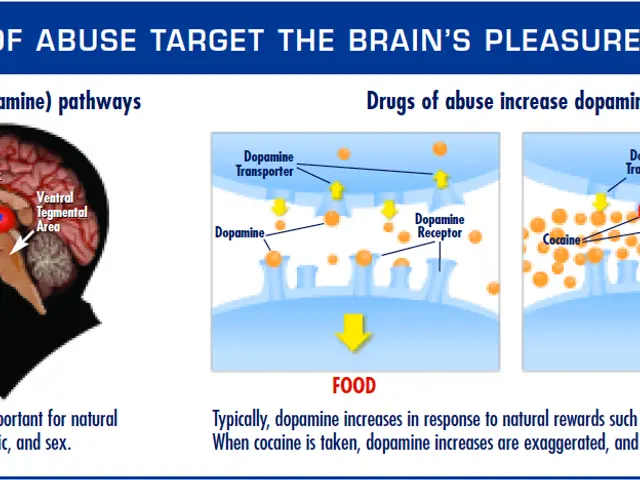
Celiac disease, an immune response gone awry to gluten, has long posed a challenge in diagnosis. Recent developments, however, have brought a new player to the field: the WBAIL-2 test. This innovative blood test could revolutionize celiac disease diagnosis, offering a less invasive and potentially biopsy-free solution.
Blood vs. Biopsy
The WBAIL-2 test, launched in a recent study, measures interleukin-2 (IL-2) released by immune cells upon exposure to gluten peptides in a test tube. Unlike traditional methods, this novel approach doesn't necessitate a gluten challenge or intestinal biopsy, making it safer and more comfortable for patients.
** Study Insights **
The test exhibited high effectiveness in confirming celiac disease, with stronger concentrations and fold change of IL-2 in those with the disease.The results displayed a correlation with age and years of adhering to a gluten-free diet.Following an oral gluten challenge, serum IL-2 levels were higher for those with celiac disease and linked to the WBAIL-2 results.Activated gluten-specific CD4+ T cells and the levels of these cells were found to correlate with the WBAIL-2 test.
Limitations and Future Research
Though promising, the study had some limitations, including a focus on adult participants and strict inclusion criteria. Additionally, while the test showed promise, its accuracy varies for certain genotypes, necessitating further study. Further research is also required to explore the test's utility in children and individuals taking immunosuppressants, as well as its reproducibility across laboratories and cost-effectiveness compared to current methods.
Expert Opinions
Doctors stress the need for larger studies and additional details regarding gluten-specific T cells to determine the WBAIL-2's clinical usefulness. They also highlight its potential as another tool in the diagnostic toolbox, complementing existing methods.
A Leap Forward in Celiac Disease Diagnosis?
With its unaided detection of celiac disease even in those on a gluten-free diet, the WBAIL-2 test shows great promise in revolutionizing the diagnostic landscape for this complex condition. Further research is needed to refine its accuracy, address its limitations, and ultimately, make celiac disease diagnosis more accessible and less invasive.
Enrichment Data Summary
The WBAIL-2 test, measuring interleukin-2 release upon exposure to gluten, exhibits high sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing celiac disease without requiring a gluten challenge or intestinal biopsy. The test's potential advantages include reduced invasiveness, higher accuracy, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. Further research is required to address limitations and expand its utility in various populations.
- The WBAIL-2 test, measuring IL-2 release upon exposure to gluten, could potentially aid in the diagnosis of other autoimmune disorders.
- The gastrointestinal system and the immune system play a significant role in the development and progression of celiac disease.
- The results of the WBAIL-2 test could have implications for the management and treatment of chronic diseases like chronic kidney disease.
- A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support the functioning of the immune system, potentially aiding in the management of celiac disease.
- CBD, a compound known for its potential immune-modulating properties, might be a topic of interest in relation to its effects on the immune response in celiac disease.
- Fitness and exercise can contribute to overall health and wellness, which may be beneficial for those managing celibac disease.
- Medical-conditions like celiac disease require a systematic and comprehensive approach, involving aspects like diagnosis, treatment, and management, in addition to lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise.