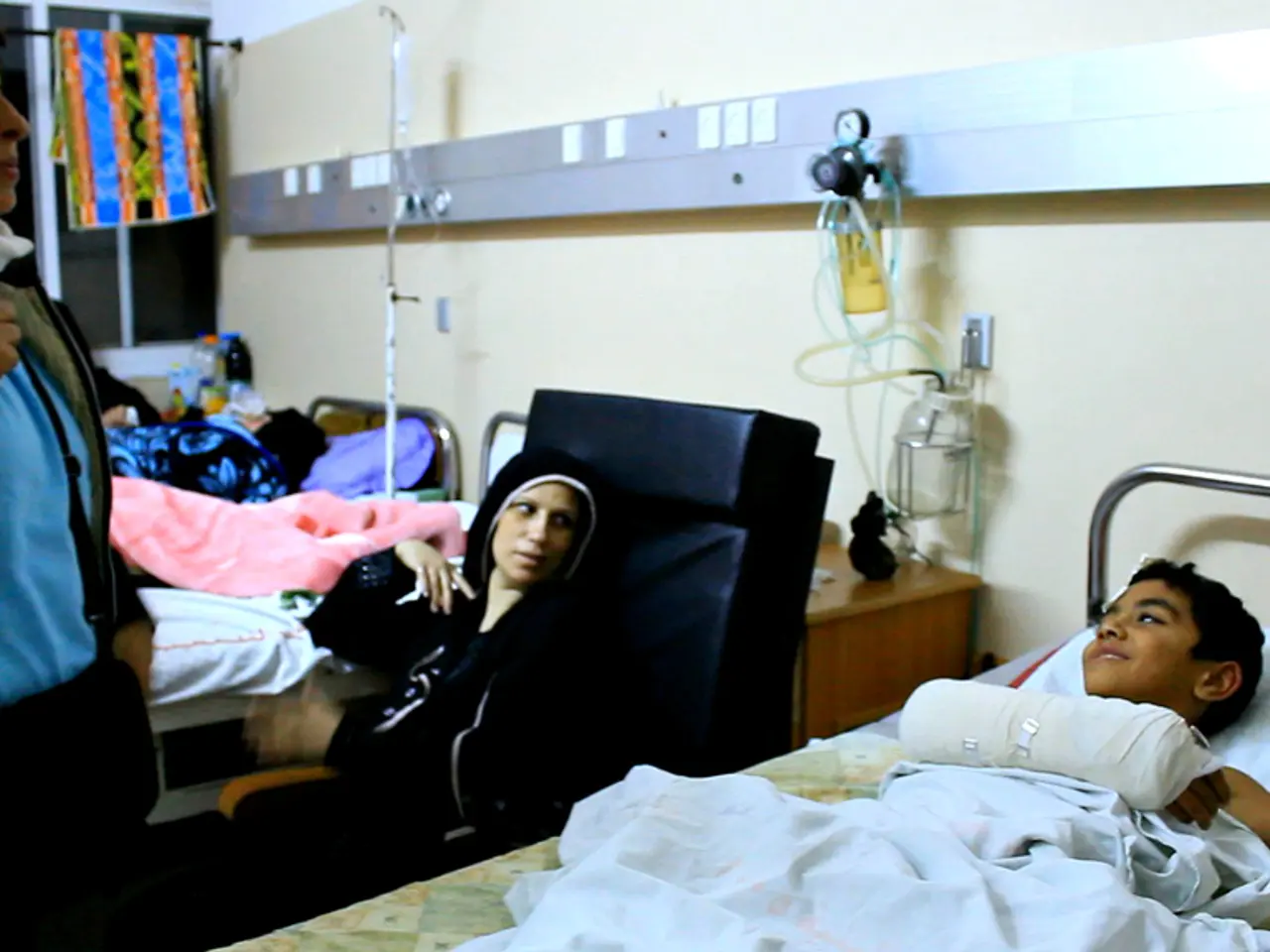
Public hospitals now prohibit shared sleeping arrangements under the latest health reforms, as decreed by Duale.
The implementation of a one-patient-one-bed policy in public hospitals across Kenya, including the Nakuru Level V Hospital (PGH), is part of a broader initiative to enhance patient care and address issues related to bed capacity.
Bed Capacity
The policy aims to prevent overcrowding and ensure that each patient has a bed, thereby promoting proper hygiene and reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections. While specific details about Nakuru Level V Hospital are not provided, the enforcement of this policy should lead to an increase in bed capacity utilization efficiently. Hospitals like Nakuru Level V might need to expand their existing bed capacity or optimize their current facilities to accommodate more patients without compromising care quality.
Patient Care
The policy enhances the overall quality of care by enabling nurses and healthcare providers to attend to patients more effectively. This is particularly important for hospitals like Nakuru Level V, where the demand for quality healthcare services is high. Additionally, the policy improves the patient experience by reducing overcrowding and promoting a more dignified environment for care, leading to higher patient satisfaction and trust in the healthcare system.
Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing the policy requires significant resource allocation, including the recruitment of more healthcare personnel and the possible expansion of hospital facilities. This presents both challenges and opportunities for hospitals to upgrade their infrastructure and staffing.
The Ministry of Health's efforts to crack down on illegal health facilities and enforce standardization of healthcare services across the country could support this policy by ensuring that all facilities, including those in Nakuru, operate within approved standards.
Case Study: Nakuru Level V Hospital
The Nakuru Level V Hospital serves as a referral center for the Rift Valley region and treats at least 2,000 patients daily, with over 750 being inpatients. The hospital's maternity wing has seen mothers sharing beds, and the ICU has only six beds, while the ideal capacity is 20. Overcrowding in general wards has led to early patient discharges, and the hospital's lack of designated isolation or emergency beds poses a significant challenge.
Despite these challenges, the one-patient-one-bed policy offers an opportunity to improve patient care at Nakuru Level V Hospital. The policy's successful implementation would require adequate support for facility upgrades and staffing adjustments to meet the increased demand for beds.
In conclusion, the one-patient-one-bed policy should lead to improved patient care and more efficient use of bed capacity in hospitals like Nakuru Level V, assuming that there is adequate support for facility upgrades and staffing adjustments.
- Incorporating health and wellness initiatives, such as workplace-wellness programs, could help employees manage chronic diseases and respiratory conditions, improving overall health.
- Eye health is crucial in maintaining quality of life, and regular eye check-ups and proper skin care can help prevent skin conditions.
- The epaper reported on new research suggesting that CBD oil may aid in managing hearing issues and mental health concerns.
- To address the increasing demand for health care services, hospitals might consider investing in fitness and exercise facilities to promote healthier lifestyles among patients.
- Ensuring proper medical conditions management is vital for reducing hospital readmissions.
- Proper sleep is essential for overall wellbeing, and getting enough rest each night can help individuals manage their health and prevent potential medical conditions.
- When dealing with health crises, such as a pandemic, it's important to have a well-prepared healthcare system capable of addressing the surge in patients while maintaining quality care.
- Reducing the strain on health care facilities can lead to shorter waiting times for patients, particularly those with chronic diseases or respiratory conditions requiring specialized care.