Regular Practices for Instructors and Overseers: Repeated Actions
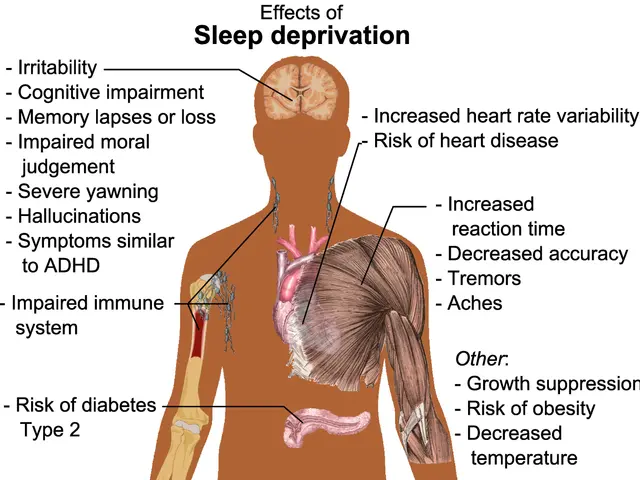
Repetitive Motion Injuries (RSIs), also known as Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTD), are a common issue that can affect anyone who engages in activities involving repeated movements. These injuries can strain muscles, tendons, or nerves, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, and other discomforts.
Common causes of RSIs include repetitive movements, poor posture, overuse without adequate rest, improper technique, and poor ergonomics in work or activity settings. Activities like typing, using a mouse, playing instruments, certain sports, and manual labor increase the risk. Jobs in manufacturing, construction, healthcare, retail, and office environments are often associated with RSIs.
Typical symptoms of RSIs include pain, cramping, swelling, throbbing, tingling, numbness, restriction of joint movement, soft tissue swelling, loss of feeling, decreased manual dexterity, stiffness, and fatigue in the affected areas, which commonly include wrists, hands, arms, shoulders, neck, and back.
Prevention strategies focus on ergonomic improvements, maintaining correct posture, taking frequent breaks, using proper techniques, incorporating exercises, and avoiding excessive force and vibration exposure. Ergonomic improvements involve using properly designed equipment and workspace setups to reduce strain.
If pain occurs despite prevention measures, it is essential to contact a doctor for an evaluation. Treatment approaches often include movement therapy, physical therapy, rest, anti-inflammatory medications, medical interventions like injections or surgery in severe or chronic cases, and personalized rehabilitation programs.
Early identification and intervention are crucial because untreated RSIs can lead to permanent disability and loss of function. Treatment may involve medication to reduce inflammation and pain, regular follow-up visits, referral to an occupational therapist, removal from the causing situation, a gradual return to an improved work situation, and strengthening hand and arm muscles with exercise.
Being aware of repetitive motion used both on and off the job and adapting work activities and the use or movement of equipment to avoid repetitive motions are key prevention measures. Remember, prevention is better than cure, so taking care of your body and adopting good habits can help you avoid the discomfort and potential long-term effects of RSIs.
Read also:
- Impact of Alcohol Consumption During Pregnancy: Consequences and Further Details
- The cause behind increased urination after alcohol consumption is explained here.
- Toe joint arthritis: Signs, triggers, and further details
- West Nile Virus found in Kentucky for the first time; residents advised to take protective measures