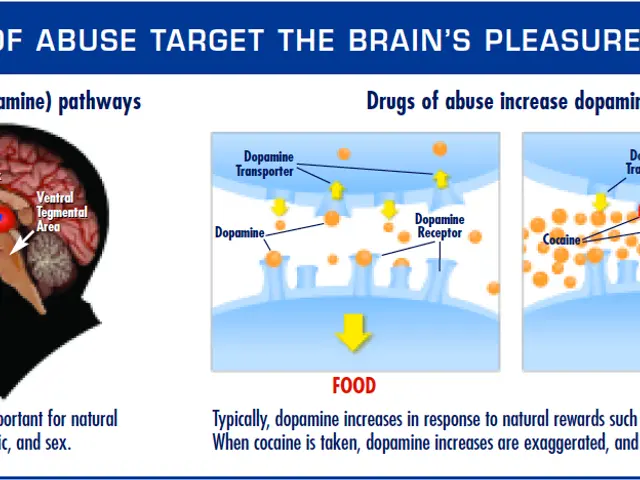
Umbilical cord blood stem cells: Information on these vital cells found in newborns' umbilical cords and their potential medical applications.
Umbilical cord blood stem cells, a type of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) found in the umbilical cord of newborns, are becoming a valuable resource for future medical treatment. These special cells, which can develop into different cell types, have been shown to promote cardiac repair and improve cardiac function, have anti-tumor properties, and promote neural repair and regeneration.
These cells are collected from the cord blood after birth, offering advantages over other sources of stem cells, including ease of access, reduced likelihood of causing an immune response, and flexibility. Research is ongoing into the use of umbilical cord blood stem cells to treat various diseases and disorders, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and neurological disorders.
The future of umbilical cord blood stem cells is promising, with ongoing research and development in the field of regenerative medicine and stem cell therapy. These cells have immunomodulatory effects, meaning they can help regulate the immune system and prevent rejection of transplanted cells, making them particularly useful in transplantation procedures.
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are stored in cryopreservation facilities and can be a valuable resource for future medical treatment. The cost of umbilical cord blood stem cell banking varies depending on the type of bank and the services offered.
In Germany, institutions that collect and store umbilical cord blood stem cells include various university hospitals and specialized cord blood banks, such as the Universitätsklinikum Jena. These centers focus on collection, processing, and long-term storage for medical use and research purposes.
Currently, umbilical cord blood stem cells are being used to treat a range of blood disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia. They have the potential to revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine by repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs, promoting healing and regeneration.
Moreover, umbilical cord blood stem cells are being explored for their potential uses in regenerative medicine, immunotherapy, and cancer treatment, including the treatment of heart disease, diabetes, neurological disorders, orthopedic injuries and diseases, autoimmune disorders, graft-versus-host disease, and various types of cancer.
MSCs, like umbilical cord blood stem cells, have anti-inflammatory properties, promote tissue repair, and modulate the immune system. The advantages of using umbilical cord blood stem cells over bone marrow transplants in terms of collection, processing, and transplantation are significant, with a lower risk of graft-versus-host disease and the ability to be frozen and stored for extended periods.
Research on umbilical cord blood stem cells is ongoing, with scientists continuing to explore their potential uses in treating various diseases and disorders. The future of medicine may well lie in the hands of these versatile and promising cells.
Read also:
- European Commission introduces communication on strategies for protecting democracy and fundamental rights online
- Exploring the Health Benefits of Consuming Plum Liqueur Infused with Oats and Almonds
- Europe's mandatory vaccination programs advocated by health officials in the face of mounting disinformation
- Rural farm communities sound the alarm over the perilous state of livestock deliveries