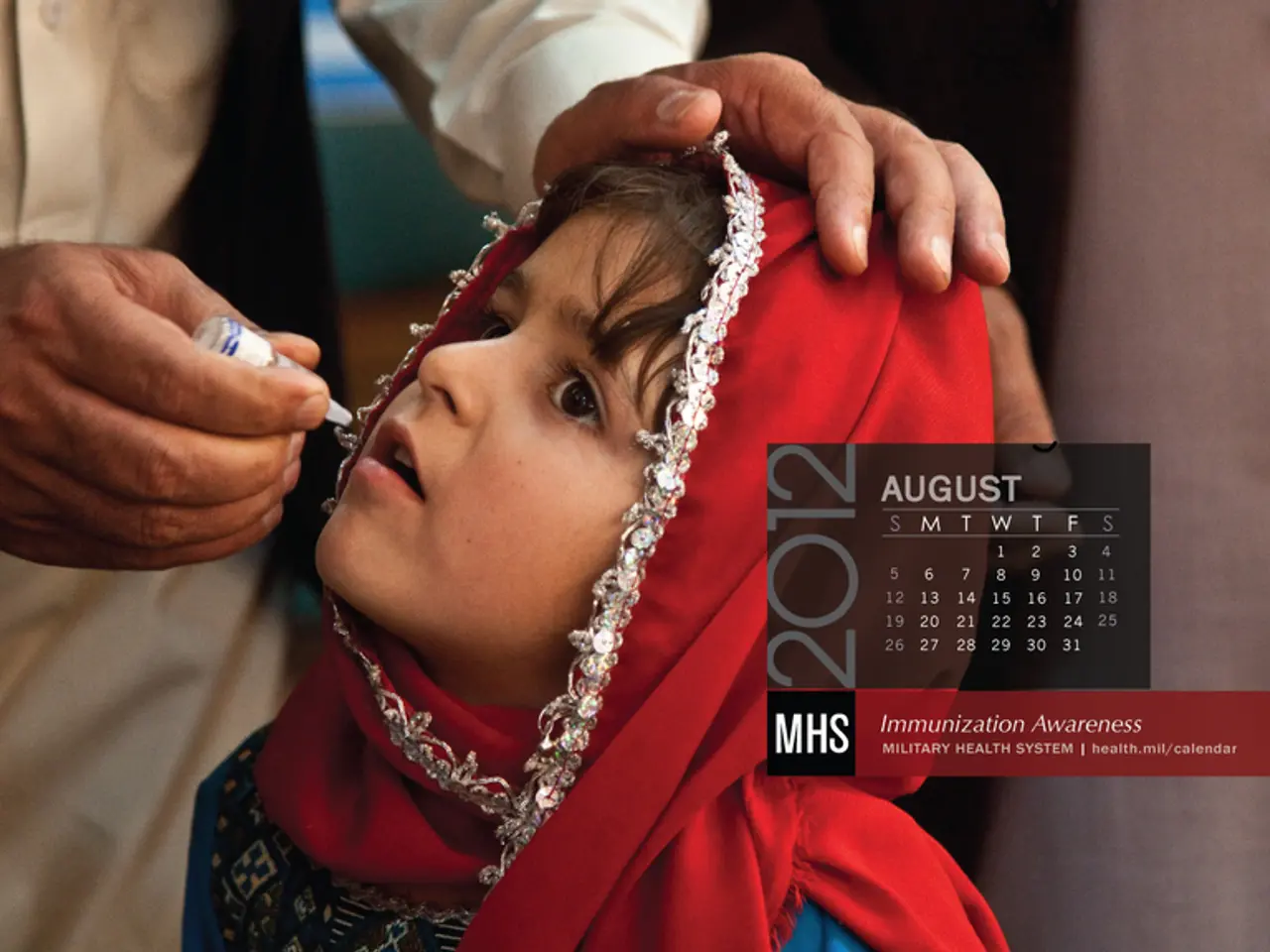
Vaccination with and without Medical Recommendation for COVID-19
In the ongoing battle against the COVID-19 pandemic, the vaccination landscape is evolving, with different recommendations emerging for various age groups across the globe. In Germany, the Standing Vaccination Commission (Stiko) has recently adjusted its guidelines, raising questions about the vaccination frequency for healthy children and adolescents.
While the specific rationale for this decision remains unclear, several factors typically influence such decisions. These include the risk assessment, vaccine efficacy and safety, public health goals, and long-term effects.
The risk of severe illness from COVID-19 in healthy children is generally low compared to older populations or those with underlying health conditions. As a result, the urgency to increase vaccination frequency might be less pressing in this demographic.
Ensuring safety and avoiding unnecessary side effects is a priority when it comes to vaccinating children. The effectiveness and safety of vaccines in different age groups are crucial considerations.
Vaccination policies are designed to protect vulnerable populations and prevent disease spread. The focus on high-risk groups ensures that limited resources are used efficiently. However, the long-term effects of COVID-19, such as Long Covid and Post Covid, may not be as prevalent in healthy children as in other populations. This factor might weigh the current evidence on these conditions against the need for higher vaccination rates in this demographic.
Brandenburg's Health Minister, Britta Müller (BSW), has promised support for those affected by COVID-19, emphasising the importance of listening to the concerns of the public. Federal Minister of Health, Karl Lauterbach, has tweeted that the Stiko recommendation provides a good basis for protecting the population from the consequences of further COVID infections.
Meanwhile, the European vaccination commission continues to recommend vaccination for all age groups, unlike in Germany. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has adjusted its vaccination guidelines, recommending a second booster for the elderly and immunocompromised, and vaccination with the adapted active ingredient for everyone over six years old, regardless of their previous vaccination status.
As the pandemic continues, the focus remains on understanding and addressing the long-term effects of COVID-19. An estimated 20 million people in Europe are now affected by long-covid, with up to ten percent experiencing long-term and difficult-to-treat problems. Recent findings from a large meta-analysis of studies published in the UK last month showed a 43 percent reduction in long-covid risk after two doses of vaccination.
However, the debate around vaccination for children is not without controversy. The withdrawal of vaccination recommendations for children is being used by vaccine opponents to create fear and guilt among parents. It is crucial to approach these decisions with a clear understanding of the facts and the considerations that influence them.
As the situation continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed and follow the advice of health authorities. For now, the Stiko recommendation aims to prevent severe COVID-19 cases, reduce possible long-term effects of Sars-CoV-2 infections, and protect healthcare workers from Sars-CoV-2 infections.
- The debate surrounding the adjustment of vaccination guidelines for children in Germany, as recently done by the Standing Vaccination Commission (Stiko), is influenced by factors such as risk assessment, vaccine efficacy and safety, public health goals, long-term effects, and political considerations that include policy-and-legislation and politics.
- The general-news about the estimated 20 million people in Europe affected by long-covid, with up to ten percent experiencing long-term and difficult-to-treat problems, highlights the importance of understanding and addressing the long-term effects of COVID-19, including through nutrition and health-and-wellness practices.
- In the context of the evolving vaccination landscape in the ongoing battle against COVID-19, the focus on science and evidence-based decision-making, such as in the Stiko recommendation, is crucial to ensure the safety, health, and wellness of all age groups, while also considering policy-and-legislation and political factors.